For small to medium businesses, startups, and creative teams, managing vendor relationships is more than an administrative task; it's a strategic imperative. The right partnerships can fuel growth, spark innovation, and provide a significant competitive edge. However, without a structured approach, vendor management can quickly become a source of risk, inefficiency, and wasted resources. This guide moves beyond generic advice to provide a deep dive into eight actionable vendor management best practices.
We will explore how to build a resilient and value-driven vendor ecosystem, from initial due diligence to fostering collaborative innovation. You will learn specific, practical methods to transform your vendor engagements from simple transactions into powerful, strategic assets for your organization. For businesses expanding their reach, understanding the nuances of strategic offshore vs. nearshore sourcing decisions is also crucial for effective global vendor management and cost optimization.
This article provides a clear roadmap to help you select, manage, and grow with your vendor partners, ensuring every relationship contributes directly to your bottom line and long-term success. Let's begin building a more robust framework for your vendor partnerships.
1. Comprehensive Vendor Due Diligence and Risk Assessment
One of the most foundational vendor management best practices is establishing a systematic process for evaluating potential partners before signing any contracts. Comprehensive due diligence goes beyond a simple price comparison; it's a deep-dive investigation into a vendor's stability, security posture, and overall reliability. This practice is crucial for mitigating risks that could lead to financial loss, data breaches, or operational disruptions.
This foundational step involves a multi-layered screening process. By thoroughly examining a vendor's financial health, security protocols, regulatory compliance, and operational capabilities, you ensure they can meet contractual obligations and won't introduce unforeseen liabilities into your organization. It's about building partnerships on a bedrock of trust and verified information rather than assumptions.
Key Components of Due Diligence
A robust due diligence process typically includes several key areas of investigation:
- Financial Stability: Assessing a vendor's financial health helps confirm they have the resources to deliver on their promises consistently. This can involve reviewing financial statements or using third-party services for credit assessments.
- Security Practices: For any vendor that will handle your data, evaluating their security measures is non-negotiable. This includes looking at their data encryption, access controls, and incident response plans.
- Compliance Verification: Ensure potential vendors comply with relevant industry regulations and legal standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2. This protects your business from legal and reputational damage.
- Operational Capability: Can the vendor actually do what they say they can do? This involves assessing their track record, checking references, and understanding their capacity to handle your business volume.
The following visual breaks down a simplified, sequential workflow for this initial screening process.
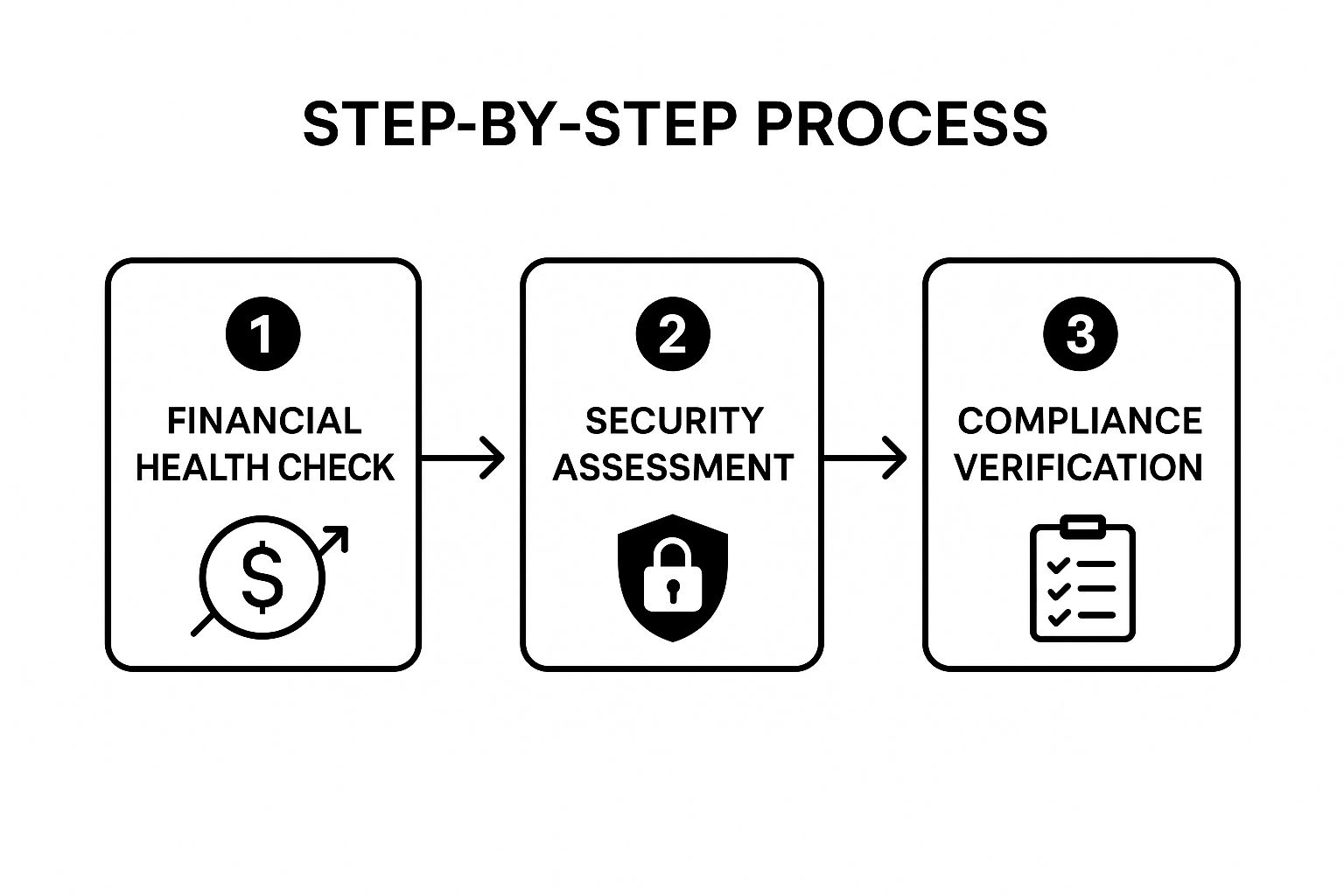
This process flow visualizes a logical sequence, ensuring that foundational checks on financial and security viability are completed before moving to more specific compliance requirements.
2. Structured Vendor Lifecycle Management
Adopting a structured approach to the entire vendor relationship is a core element of effective vendor management best practices. This means managing partners through distinct, well-defined phases, from initial identification and onboarding to ongoing performance management and eventual offboarding. Structured vendor lifecycle management transforms reactive vendor interactions into a proactive, strategic process.
This comprehensive framework ensures consistency, proper documentation, and strategic alignment at every touchpoint. By viewing the relationship as a full cycle rather than a one-time transaction, organizations can maximize value, maintain control, and systematically improve vendor collaborations over time. This approach is fundamental to building resilient and high-performing supply chains, particularly in dynamic environments like creative agencies and startups. To explore how this fits into a broader operational framework, you can learn more about creative operations management.
Key Stages of the Vendor Lifecycle
A well-defined vendor lifecycle ensures no steps are missed and that accountability is clear throughout the partnership. The primary stages include:
- Identification and Onboarding: This initial phase involves sourcing, vetting, and formally bringing a new vendor into your systems. It includes contract negotiation, setting up payment details, and integrating them into your workflows.
- Performance and Relationship Management: The longest phase involves continuously monitoring vendor performance against service-level agreements (SLAs), conducting regular reviews, and fostering a collaborative relationship.
- Risk and Compliance Monitoring: Throughout the partnership, you must regularly assess and mitigate risks, ensuring the vendor remains compliant with industry standards and contractual obligations.
- Renewal or Offboarding: At the end of a contract term, a formal decision is made to either renew the agreement or begin a structured offboarding process, which includes data hand-offs and final payments.
The following video provides an excellent overview of the key considerations for managing the vendor lifecycle effectively.
By implementing these distinct stages, your organization can create a repeatable and scalable process for managing every vendor with precision and strategic foresight.
3. Centralized Vendor Information Management System
Another essential vendor management best practice is implementing a unified platform to consolidate all vendor-related information. A centralized system acts as a single source of truth, housing contracts, performance data, compliance documents, and communication history in one accessible repository. This approach is critical for eliminating information silos, reducing duplicate efforts, and enabling consistent oversight across the organization.
By centralizing data, you move away from scattered spreadsheets and email chains toward a structured, reliable information hub. This allows for better decision-making, improved cross-departmental collaboration, and enhanced strategic planning. Companies like Salesforce and ServiceNow have popularized platforms that provide this exact functionality, proving its value at scale.

Key Components of a Centralized System
An effective vendor information system should be more than just a digital filing cabinet. It needs to provide actionable intelligence and streamline workflows.
- Contract Repository: Store all contracts, amendments, and key dates (like renewals and expirations) in one place. Set up automated alerts to ensure you never miss a critical deadline.
- Performance Tracking: Integrate performance metrics and scorecards directly into the vendor profile. This allows you to track KPIs over time and make data-driven decisions about contract renewals.
- Compliance Documentation: Maintain up-to-date records of all compliance and security documents, such as SOC 2 reports, ISO certifications, and insurance certificates, ensuring your partners meet required standards.
- Communication Log: Keep a detailed history of all significant communications, from initial negotiations to ongoing support tickets. This provides valuable context for anyone interacting with the vendor.
For creative teams, this level of organization is particularly vital for managing contractors and suppliers. By integrating this system with your existing workflows, you can streamline project execution. Learn more about creative resource management at Creativize.
4. Performance-Based Vendor Management with KPIs
Another essential vendor management best practice is shifting from a relationship-based approach to a data-driven one. Performance-based management uses clear metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to objectively measure how well vendors meet agreed-upon standards. This practice fosters transparency and accountability, ensuring that vendor relationships deliver tangible value rather than just fulfilling a contract.

This method moves beyond subjective feelings about a vendor and relies on hard data. By establishing a framework for regular performance reviews, scorecards, and improvement planning, you can ensure vendors consistently meet or exceed expectations. It's about creating a partnership where both parties are aligned on what success looks like and are committed to achieving it. A core component of this is ensuring effective project quality management for all vendor deliverables.
Key Components of Performance-Based Management
A strong performance management system is built on a foundation of clear, mutually understood metrics. This approach is exemplified by companies like Toyota, which uses a robust supplier evaluation system focused on quality, delivery, and cost.
- SMART KPIs: Develop KPIs that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. For a creative agency vendor, this might be "Achieve a 95% client satisfaction score on all projects delivered in Q3."
- Collaborative Goal Setting: Involve vendors in the KPI development process. This collaboration ensures the metrics are realistic and promotes vendor buy-in, making them a partner in the process rather than just a subject of evaluation.
- Regular Performance Reviews: Schedule consistent reviews (e.g., quarterly) to discuss performance data. Use these meetings to address challenges, recognize achievements, and collaboratively plan for improvements.
- Balanced Scorecards: Use a mix of leading indicators (e.g., response times) and lagging indicators (e.g., final project ROI) to get a complete picture of vendor performance. To see how this works in a specific field, you can review some common digital marketing performance metrics.
5. Strategic Vendor Relationship Segmentation
A highly effective vendor management best practices approach involves not treating all suppliers equally. Strategic vendor segmentation is the process of categorizing vendors based on their strategic importance, spend levels, and associated risks. This allows you to allocate management resources efficiently, focusing your efforts where they matter most and tailoring your engagement model to fit the nature of each partnership.
This practice moves beyond a one-size-fits-all strategy. By classifying your vendors, from critical strategic partners to transactional suppliers, you can develop distinct management playbooks for each group. This ensures that high-value, high-risk relationships receive the attention they deserve, while lower-impact vendors are managed in a more streamlined, cost-effective manner.
Key Components of Vendor Segmentation
A robust segmentation model, often inspired by Peter Kraljic's purchasing portfolio matrix, helps create clear categories and management strategies for each.
- Strategic Partners: These are high-spend, high-risk vendors critical to your core business operations or product innovation. They require close collaboration, executive-level engagement, and joint business planning. An example is Apple's deep integration with a key component supplier like TSMC.
- Preferred Vendors: These vendors are important and may represent significant spend, but they are more easily replaceable than strategic partners. The goal here is to build strong relationships and negotiate favorable terms, but with less intensive oversight.
- Transactional Suppliers: This category includes low-spend, low-risk vendors providing standard, off-the-shelf goods or services. Management should be highly efficient, often automated through procurement platforms to minimize administrative overhead.
- High-Risk/Low-Spend Vendors: These suppliers may not account for a large portion of your budget but pose a significant risk (e.g., a sole-source provider for a minor but essential component). They require diligent risk monitoring and contingency planning.
6. Proactive Contract Management and Compliance Monitoring
One of the most critical vendor management best practices involves moving from reactive to proactive contract oversight. This means actively managing vendor agreements throughout their entire lifecycle, rather than filing them away until a problem arises. Proactive contract management establishes a system for tracking key dates, monitoring deliverables, and ensuring ongoing compliance with all agreed-upon terms.
This strategic approach transforms contracts from static documents into dynamic management tools. By systematically monitoring performance against contractual obligations, you can mitigate risks, prevent value leakage, and identify opportunities for optimization or renegotiation. It ensures that the value you signed up for is the value you actually receive, safeguarding your business from missed deadlines, scope creep, and non-compliance penalties.
Key Components of Contract Management
A robust contract management framework is built on continuous and systematic oversight. Here are the core elements to implement:
- Centralized Contract Repository: Store all vendor contracts in a single, secure, and accessible location. This prevents lost documents and provides a single source of truth for all stakeholder inquiries.
- Automated Milestone Tracking: Use software or a detailed calendar system to set up automated alerts for critical dates. This includes contract renewal deadlines, termination notice periods, and key deliverable dates.
- Compliance and Performance Audits: Regularly audit vendor performance against the specific terms, service levels, and key performance indicators (KPIs) outlined in the contract. This verifies that vendors are meeting their obligations.
- Standardized Templates and Clauses: Develop and use standardized contract templates and pre-approved legal clauses. This streamlines the creation and negotiation process, reduces legal risk, and ensures consistency across all your vendor agreements. Just as you might use a template for a project communication plan to ensure clarity, standardized contracts enforce consistency in your vendor relationships.
This systematic process ensures that no contractual detail is overlooked, turning your agreements into powerful tools for driving vendor value and accountability.
7. Integrated Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Another critical vendor management best practice involves moving beyond initial due diligence to a continuous cycle of risk assessment and preparedness. Integrated risk management is a holistic approach to identifying, evaluating, and mitigating potential vendor-related threats throughout the entire lifecycle of the partnership. It's not a one-time check, but an ongoing process designed to ensure business continuity.
This forward-thinking practice involves proactively planning for potential disruptions, such as a vendor's sudden service failure, a security breach, or even bankruptcy. By developing robust contingency plans, your organization can pivot quickly, minimizing operational downtime, financial losses, and reputational damage. This approach shifts vendor management from a reactive, problem-solving function to a strategic, protective one.

Key Components of Risk Management and Contingency Planning
A strong risk management framework anticipates problems before they occur. Key areas of focus include:
- Risk Identification and Assessment: Regularly update a risk register that catalogs potential vendor risks, from operational and financial to cybersecurity and compliance. Each risk should be assessed for its potential impact and likelihood, then assigned a clear owner responsible for its mitigation. For example, after its 2013 data breach, Target significantly enhanced its third-party risk management program to continuously monitor vendor security postures.
- Contingency and Exit Strategy Development: For every critical vendor, you must have a "Plan B." This includes identifying and vetting alternative suppliers, documenting a clear exit strategy for transitioning away from the current vendor if necessary, and ensuring you can retrieve your data securely.
- Scenario Planning and Testing: Don't just create plans; test them. Regularly conduct simulations or tabletop exercises to test your response to various failure scenarios, such as a key supplier going offline. This helps identify gaps in your strategy before a real crisis hits.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement tools and processes to monitor key risk indicators (KRIs) in real-time. This could include alerts for negative news about a vendor, changes in their financial stability, or dips in their performance metrics. To effectively safeguard your operations, delving deeper into specific tactics for managing the inherent risks in external collaborations is crucial. Consider exploring comprehensive resources on outsourcing risk management strategies.
8. Collaborative Vendor Development and Innovation Programs
Moving beyond transactional relationships, one of the most strategic vendor management best practices is to actively cultivate vendor capabilities through collaborative development and innovation. This advanced approach treats select suppliers as true partners in growth, moving from a simple procurement model to a co-creation ecosystem. It involves joint planning, shared investments, and knowledge transfer to build a stronger, more innovative supply chain that benefits both parties.
This practice transforms the vendor relationship into a source of competitive advantage. Instead of merely managing performance against a contract, you are actively investing in a vendor's ability to innovate and improve. This creates a deeply integrated partnership where vendors contribute directly to your product development, process improvements, and long-term strategic goals, such as those seen in Toyota's legendary supplier development programs.
Key Components of Vendor Development
Implementing a successful collaborative program requires structure and commitment. Key areas to focus on include:
- Joint Business Planning: Involve strategic vendors in your long-term planning sessions. Share your roadmap and challenges to identify areas where their expertise can drive innovation and create mutual value.
- Structured Development Programs: Create formal programs with clear objectives, timelines, and measurable outcomes. This could involve training, technology sharing, or joint process improvement projects aimed at enhancing the vendor's capabilities.
- Intellectual Property (IP) Agreements: Before embarking on co-innovation, establish clear and fair agreements regarding the ownership of any jointly developed intellectual property. This protects both organizations and encourages open collaboration.
- Cultural Alignment and Growth Potential: Select partners who not only have the potential to grow but also share your company's values and vision. A strong cultural fit is essential for the trust and transparency required for these deep partnerships, much like building a strong community. You can find similar principles in guides on effective community engagement strategies.
Best Practices Comparison of 8 Vendor Management Strategies
| Vendor Management Approach | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive Vendor Due Diligence and Risk Assessment | High 🔄🔄 | High ⚡⚡ | Reduced vendor risks, improved compliance, better vendor quality | Pre-partnership evaluation, high-risk vendor sectors | Risk mitigation, regulatory adherence, reputational protection |
| Structured Vendor Lifecycle Management | Medium-High 🔄🔄 | Medium-High ⚡⚡ | Standardized processes, lifecycle visibility, proactive management | Entire vendor relationship duration | Consistency, planning, reduced admin overhead |
| Centralized Vendor Information Management System | Medium 🔄 | Medium ⚡ | Unified data access, improved decisions, better collaboration | Managing large vendor datasets, cross-department use | Data consistency, audit readiness, reduced duplication |
| Performance-Based Vendor Management with KPIs | Medium-High 🔄🔄 | Medium ⚡⚡ | Objective performance insight, continuous improvement | Performance-sensitive contracts, accountability focus | Transparency, early issue detection, improvement facilitation |
| Strategic Vendor Relationship Segmentation | Medium-High 🔄🔄 | Medium ⚡⚡ | Optimized resource allocation, improved risk management | Diverse vendor portfolios, spend management | Efficiency, strategic focus, enhanced negotiation leverage |
| Proactive Contract Management and Compliance Monitoring | Medium 🔄 | Medium ⚡ | Avoid missed deadlines, compliance assurance, cost control | Contract-heavy environments | Risk reduction, process automation, budget predictability |
| Integrated Risk Management and Contingency Planning | High 🔄🔄 | High ⚡⚡ | Business continuity, early warnings, crisis response | High-risk/dynamic supplier environments | Resilience, regulatory compliance, crisis mitigation |
| Collaborative Vendor Development and Innovation Programs | High 🔄🔄 | High ⚡⚡ | Innovation growth, stronger partnerships, supply chain capability | Strategic partnerships, innovation-driven sectors | Competitive advantage, capability building, long-term value |
From Management to Mastery: Building Your Vendor Advantage
Navigating the landscape of vendor management can feel complex, but as we have explored, a structured and strategic approach transforms it from a necessary administrative task into a powerful competitive advantage. The journey from simple vendor management to true vendor mastery is built upon the consistent application of a core set of principles. It’s about shifting your organizational mindset, moving away from purely transactional relationships and embracing a new paradigm of strategic partnership and mutual growth.
Implementing these vendor management best practices is not about adopting a rigid, one-size-fits-all system. Instead, it’s about creating a flexible, resilient framework tailored to your unique business needs. Whether you're a startup securing foundational software services or a creative agency collaborating with freelance talent, the core tenets remain the same: clarity, communication, and continuous improvement.
Recapping Your Path to Vendor Excellence
The practices detailed in this article form a comprehensive toolkit for building a robust vendor ecosystem. Let's revisit the essential pillars:
- Foundation First: It all begins with Comprehensive Due Diligence and a Structured Vendor Lifecycle. You wouldn't build a house on an unstable foundation, and you shouldn't build your business on unvetted or poorly managed partnerships.
- Systemize and Centralize: Implementing a Centralized Information Management System eliminates chaos. It ensures that critical data, from contracts to performance reviews, is accessible, secure, and actionable, preventing costly knowledge gaps.
- Measure and Segment: You cannot improve what you do not measure. By establishing clear Performance-Based KPIs and employing Strategic Vendor Segmentation, you can focus your most valuable resources on your most critical partners, maximizing ROI and fostering deeper collaboration.
- Mitigate and Innovate: Finally, proactive Contract Management and Integrated Risk Planning protect your business from potential disruptions. This secure foundation then allows you to move beyond maintenance and into Collaborative Innovation Programs, turning your vendor relationships into a source of new ideas and market-leading solutions.
Your Actionable Next Steps
Mastering your vendor relationships is a marathon, not a sprint. The key to success is to start small and build momentum. Do not feel overwhelmed by the need to implement everything at once.
Begin by identifying your single biggest pain point. Is it disorganized contract renewals? A lack of visibility into vendor performance? Start there.
- Select One Practice: Choose the single best practice that addresses your most pressing challenge. For many small businesses, this is often centralizing information or establishing basic performance metrics.
- Pilot the Program: Test the new process with a single, high-impact vendor or a small group of suppliers. This allows you to refine your approach and demonstrate value before a full-scale rollout.
- Iterate and Expand: Once you have a proven success, use that momentum to gradually introduce other vendor management best practices. Each successful implementation will make the next one easier, creating a virtuous cycle of improvement that strengthens your entire operation.
Ultimately, adopting these strategies is an investment in your business’s resilience, efficiency, and capacity for growth. By treating your vendors as integral partners, you unlock a new level of value that extends far beyond the goods or services they provide. You build a network of allies dedicated to your success, creating a powerful engine for sustained innovation and a definitive market advantage.
Are you looking to build powerful partnerships with elite creative freelancers? Creativize simplifies the entire process, from discovery and vetting to project management and payment, embodying the best practices of strategic vendor management. Find your next creative partner and transform your vision into reality with Creativize.

