Creative Staffing Solutions for the Modern Team
Need to optimize your team structure? This listicle provides seven staffing plan examples to help businesses like yours thrive. Learn how to build a dynamic and efficient team, whether you're a startup, small business, or creative agency. Discover staffing models for project-based work, seasonal demands, rapid growth, remote teams, lean operations, specialized skills, and succession planning. Find the perfect staffing plan example for your needs in 2025.
1. Project-Based Staffing Plan
A Project-Based Staffing Plan is a dynamic staffing model designed to assemble a team specifically tailored to the unique requirements of a particular project. Unlike permanent staffing models, this approach emphasizes flexibility and scalability, enabling organizations to quickly ramp up or down their workforce based on project demands. It typically involves engaging contractors, consultants, or temporary employees for the duration of the project, offering a cost-effective solution for short-term initiatives. This model allows businesses to access specialized skills and expertise without the commitment of long-term employment contracts, making it an attractive option for projects with defined start and end dates. This approach is particularly relevant for staffing plan examples because it offers a tailored solution to resource allocation, directly aligning personnel with project needs.

The core of a project-based staffing plan lies in its flexibility. The workforce can be scaled up or down depending on the project phase. For instance, during the initial planning stages, a smaller team might suffice. As the project progresses into development and execution, additional specialists can be brought on board. Finally, as the project nears completion, the team can be scaled down, ensuring efficient resource utilization and cost control. This dynamic approach allows for a mix of full-time employees and contractors, leveraging the strengths of both. Full-time employees can provide continuity and institutional knowledge, while contractors bring specialized expertise to address specific project requirements. Crucially, a project-based approach necessitates clearly defined start and end dates for staffing, providing transparency and predictability for both the organization and the individuals involved.
Examples of successful project-based staffing abound across diverse industries. Software development companies frequently hire freelance developers for specific app launches, tapping into a global talent pool and gaining access to niche coding skills. Similarly, construction firms routinely assemble project-specific teams, bringing in architects, engineers, and construction workers for the duration of a building project. Marketing agencies also utilize this model, bringing in specialists for targeted campaign launches, such as SEO experts, content creators, and social media managers. These examples highlight the versatility and effectiveness of project-based staffing across different sectors.
This staffing model offers numerous advantages. It's remarkably cost-effective for short-term projects, eliminating the overhead associated with permanent employees, such as benefits and long-term salary commitments. It provides access to a wide pool of specialized expertise without the need for permanent hiring, allowing organizations to quickly assemble teams with the precise skills needed for a project. Further, it reduces overhead costs during non-project periods, as contractors are only engaged when their skills are required. Finally, it offers the flexibility to adjust team composition as the project evolves, ensuring the right talent is available at the right time.
However, project-based staffing also presents certain challenges. Potential knowledge loss occurs when contractors leave, taking their project-specific insights with them. Hourly rates for temporary staff can sometimes be higher than salaries for permanent employees. Onboarding new team members for each project requires a time investment, and integrating temporary staff into the existing company culture can be difficult. Understanding these potential drawbacks is crucial for successful implementation.
To effectively utilize project-based staffing, consider these actionable tips: Create detailed job descriptions for each project role to attract the right talent. Establish clear communication protocols for mixed teams of employees and contractors to ensure smooth collaboration. Plan for knowledge transfer sessions to retain valuable project insights. Finally, cultivate relationships with reliable contractors for future projects, building a network of trusted professionals you can readily engage. Learn more about Project-Based Staffing Plan By carefully considering these factors, organizations can leverage the power of project-based staffing to achieve project success while maintaining flexibility and cost-effectiveness. This makes it a highly valuable staffing plan example, especially for organizations navigating fluctuating project demands and specialized skill requirements.
2. Seasonal Staffing Plan
A seasonal staffing plan is a workforce strategy designed to address predictable fluctuations in business demand throughout the year. This staffing plan examples focuses on optimizing workforce size by hiring temporary or part-time workers during periods of high demand, often referred to as peak seasons, and reducing staff during slower periods. This cyclical approach to staffing is particularly common in industries like retail, hospitality, tourism, agriculture, and shipping, where demand is heavily influenced by seasonal factors like holidays, weather patterns, or specific events.

This staffing plan example hinges on several key features. Predictable hiring and layoff cycles are established based on historical data and projected demand. Effective integration of temporary and permanent staff is essential to maintain operational efficiency and consistent service quality. Training programs designed for quick onboarding ensure that seasonal workers can rapidly contribute to the team. Inventory management needs to be closely aligned with staffing levels to ensure that adequate resources are available to meet customer demand during peak seasons. Finally, performance metrics should be adapted for seasonal workers to fairly assess their contributions during their shorter tenure.
Seasonal staffing offers several compelling advantages. Perhaps the most significant is optimal cost management. By scaling your workforce up or down in direct response to demand, you avoid the expense of carrying a full-time staff during slower periods. This flexibility allows businesses to handle peak season workloads effectively without overspending on labor. The influx of temporary workers also provides an opportunity to evaluate potential candidates for permanent positions, offering a built-in trial period for both the employer and employee. Finally, reduced labor costs during off-peak times contribute to improved profitability and financial stability.
However, a seasonal staffing plan also presents some challenges. Recruitment and training costs can be substantial each season as new workers are brought on board. The constant influx of new staff can lead to inconsistent service quality, potentially impacting customer satisfaction. Furthermore, businesses may experience increases in unemployment insurance costs due to the cyclical nature of seasonal employment. Finally, maintaining a consistent company culture can be difficult with a rotating workforce, posing challenges for team cohesion and employee engagement.
Several real-world staffing plan examples illustrate the effective implementation of seasonal strategies. Major retailers like Target and Walmart famously hire tens of thousands of seasonal workers to manage the surge in demand during the holiday shopping season. Ski resorts significantly increase their staff during the winter months to handle operations, guest services, and ski instruction. Tax preparation services like H&R Block bolster their workforce during tax season to meet the increased need for tax filing assistance. Similarly, Amazon and other e-commerce giants rely heavily on seasonal fulfillment workers to process and ship orders during peak periods like the holiday season and Prime Day sales events. These examples demonstrate how diverse businesses across various sectors utilize seasonal staffing to align their workforce with fluctuating demand.
For businesses considering a seasonal staffing plan, several tips can improve implementation and mitigate potential drawbacks:
- Start Recruiting Early: Begin the recruitment process 2-3 months before the anticipated peak season to secure qualified candidates in a competitive labor market.
- Streamlined Training: Develop concise and effective training programs that quickly equip seasonal workers with the necessary skills and knowledge.
- Incentivize Returning Workers: Offer incentives, such as bonuses or preferential scheduling, to encourage experienced seasonal employees to return for subsequent seasons, reducing recruitment and training costs.
- Maintain a Candidate Database: Keep a database of past seasonal workers who have demonstrated strong performance. This provides a readily available pool of qualified candidates for future hiring needs.
A seasonal staffing plan is a valuable workforce strategy for businesses experiencing predictable fluctuations in demand. It allows for optimal cost management, efficient handling of peak workloads, and the opportunity to evaluate potential permanent employees. However, it’s essential to carefully consider the potential downsides, such as increased recruitment costs and potential challenges in maintaining service quality and company culture. By understanding the nuances of this approach and implementing the provided tips, businesses can successfully leverage seasonal staffing to achieve their operational and financial goals. This makes it a valuable example in our exploration of various staffing plan approaches, especially for those in industries with clear seasonal demand patterns.
3. Growth-Phase Staffing Plan
For rapidly expanding organizations, a well-defined staffing plan is crucial for navigating the complexities of scaling a workforce. A Growth-Phase Staffing Plan provides a strategic hiring approach designed to systematically increase headcount while maintaining operational efficiency and nurturing company culture. This method deserves its place in this list because it provides a structured framework for sustainable organizational capacity building, aligning recruitment phases with key business growth milestones. Learn more about Growth-Phase Staffing Plan
This approach is characterized by its phased hiring process, intrinsically tied to revenue or customer acquisition targets. Unlike reactive hiring, where positions are filled as needed, a growth-phase plan anticipates future needs and proactively builds talent pipelines. This proactive approach allows businesses to maintain momentum and capitalize on market opportunities without being hampered by staffing limitations. It emphasizes not just filling roles, but finding individuals who are both a strong cultural fit and possess the potential to scale with the company. This plan also recognizes the importance of a balanced team, incorporating a mix of experienced senior hires who can provide leadership and mentorship, alongside junior development roles that contribute to long-term growth and succession planning. Furthermore, a crucial element of this plan is the inclusion of infrastructure planning. This proactive approach ensures that workspace and technology resources are scaled in tandem with headcount growth, preventing bottlenecks and maintaining productivity. Finally, integrated performance management systems are vital for providing feedback, tracking progress, and ensuring accountability during periods of rapid scaling.
Successful implementations of this model can be seen in the growth trajectories of companies like Airbnb and Uber. Airbnb's systematic approach to hiring during its global expansion phases allowed them to maintain a consistent brand experience across diverse markets. Similarly, Uber’s city-by-city staffing strategy demonstrated the effectiveness of phased hiring tied to specific market penetration goals. Tech startups often employ this strategy, scaling their engineering teams after successful funding rounds to accelerate product development and market reach. E-commerce businesses expanding to new markets also benefit from this approach, ensuring they have the necessary personnel in place to support logistics, customer service, and marketing efforts.
The infographic below visualizes the core workflow of a growth-phase staffing plan. This step-by-step process flow demonstrates how achieving a revenue milestone triggers targeted hiring of both senior and junior roles, followed by a crucial onboarding and performance review stage.
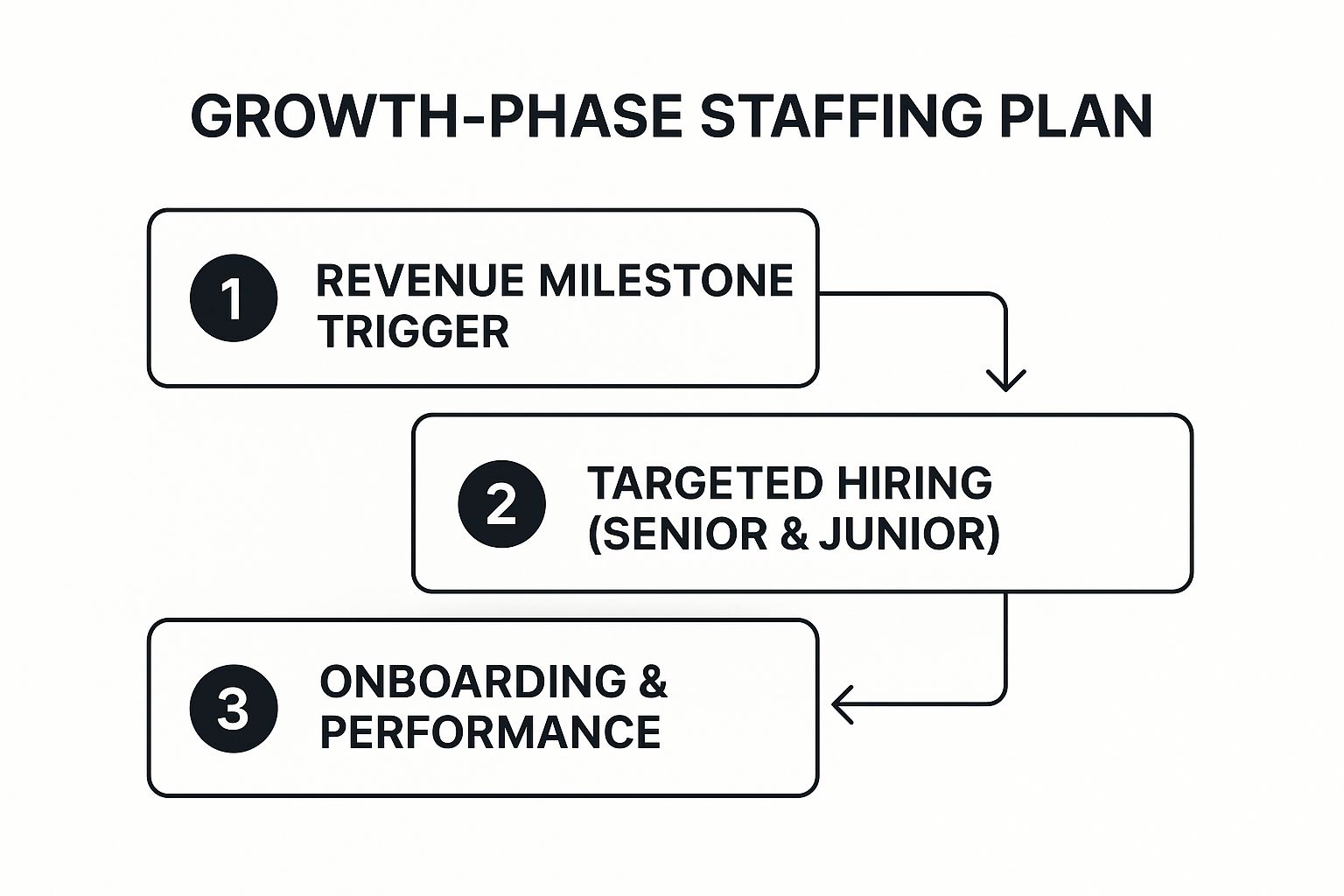
The infographic illustrates the cyclical nature of the Growth-Phase Staffing Plan, where reaching a revenue target initiates the next wave of hiring and onboarding. This iterative process ensures that staffing levels are aligned with business growth and prevents over-hiring or understaffing.
While this method offers numerous advantages, including a systematic approach to managing rapid growth, maintaining company culture during expansion, and building sustainable operational capacity, it’s important to also consider the potential drawbacks. It requires a high upfront investment in recruitment and training, and there’s a risk of over-hiring if growth projections are inaccurate. Rapid scaling can also put a strain on existing management resources and present challenges in maintaining quality control.
To effectively implement a Growth-Phase Staffing Plan, consider these actionable tips: tie hiring milestones to specific revenue or customer targets; invest in strong employer branding to attract top-tier talent; create mentorship programs to facilitate knowledge transfer and integrate new hires; establish clear promotion pathways to retain high-performing employees; and, critically, plan for infrastructure needs—office space, technology, etc.—alongside headcount growth. This approach, popularized by Silicon Valley startups like Facebook and Google, as well as unicorn companies navigating rapid scaling phases, and promoted by accelerator programs like Y Combinator, provides a robust roadmap for organizations experiencing significant expansion. By carefully considering the features, benefits, and potential challenges, and by adhering to the outlined best practices, businesses can leverage a Growth-Phase Staffing Plan to achieve sustainable and controlled growth.
4. Remote-First Staffing Plan
A remote-first staffing plan prioritizes remote work as the primary mode of operation. Instead of viewing remote work as an exception or a perk, it becomes the core of the company's operational strategy. This model focuses on hiring the best talent regardless of location and building systems and processes that support distributed teams effectively. This approach, gaining significant popularity post-COVID-19, has proven to be a viable and often preferable option for many organizations. This staffing plan example is particularly relevant for modern businesses seeking agility, cost-effectiveness, and access to a wider talent pool.

In a remote-first setup, the entire infrastructure, from communication tools to performance management systems, is designed with remote work in mind. Meetings are primarily virtual, collaboration happens through digital platforms, and company culture is fostered through online interactions and occasional in-person gatherings. This shift necessitates a conscious effort to build a strong remote work culture and ensure that all employees feel connected and supported, regardless of their physical location. It's a move away from the traditional office-centric model and embraces the flexibility and possibilities that remote work offers.
This staffing plan model deserves its place in this list due to its increasing relevance in today's business world. It offers significant advantages for both employers and employees, enabling businesses to tap into a global talent pool, reduce overhead costs, and foster a better work-life balance for their workforce. For many organizations, particularly startups, small businesses, and those in the tech industry, a remote-first approach can be a key differentiator and a driver of growth.
Features of a Remote-First Staffing Plan:
- Global Talent Pool Access: Location is no longer a limiting factor. Companies can hire talent from anywhere in the world, expanding their reach and accessing specialized skills previously unavailable.
- Digital-First Communication and Collaboration: Tools like Slack, Zoom, Asana, and Google Workspace become essential for daily communication, project management, and team collaboration.
- Flexible Work Arrangements and Time Zone Considerations: Asynchronous communication and flexible work hours become the norm, accommodating different time zones and promoting work-life balance.
- Results-Oriented Performance Management: Focus shifts from hours worked to deliverables and outcomes, promoting autonomy and accountability.
- Virtual Onboarding and Training Programs: Digital learning platforms and virtual training sessions ensure that all employees receive consistent onboarding and development opportunities.
Pros:
- Access to a Global Talent Pool: Hire the best, regardless of location.
- Reduced Office Space and Overhead Costs: Significant savings on rent, utilities, and other office-related expenses.
- Improved Work-Life Balance for Employees: Increased flexibility and autonomy can lead to greater job satisfaction.
- Higher Employee Retention Rates: A positive work environment and flexibility can contribute to retaining top talent.
- Environmental Benefits from Reduced Commuting: Lower carbon footprint due to less travel.
Cons:
- Challenges in Building Company Culture Remotely: Requires deliberate effort to foster connection and belonging.
- Potential Communication and Coordination Difficulties: Misunderstandings and delays can arise without clear communication protocols.
- Technology Infrastructure Investment Requirements: Reliable internet access, software subscriptions, and other tech investments are necessary.
- Legal and Tax Complexities with International Hires: Navigating international employment laws and tax regulations can be challenging.
- Possible Employee Isolation and Burnout: Loneliness and burnout can occur without proper support systems and work-life balance.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- GitLab: A pioneer in remote work, GitLab has a fully distributed workforce of 1,300+ employees across 65+ countries.
- Zapier: Embraced the distributed team model since its founding, demonstrating its effectiveness in scaling a remote workforce.
- Buffer: Known for its transparent remote work practices, sharing valuable insights and resources for other companies.
- Automattic (WordPress.com): A global remote workforce showcasing the scalability of this model.
Tips for Implementing a Remote-First Staffing Plan:
- Invest in robust communication and collaboration platforms: Choose tools that fit your team's needs and promote seamless communication.
- Establish clear documentation and knowledge sharing practices: Create a central repository for information and ensure easy access for all employees.
- Create structured virtual onboarding experiences: Provide new hires with a comprehensive onboarding process to integrate them into the remote culture.
- Implement regular virtual team-building activities: Foster connections and build camaraderie through online social events and team-building exercises.
- Set clear expectations for availability and response times: Establish clear guidelines to manage communication and ensure timely responses.
When considering staffing plan examples, the remote-first approach offers a powerful solution for businesses seeking to adapt to the evolving world of work. By embracing this model and implementing the strategies outlined above, organizations can unlock the full potential of a distributed workforce and position themselves for success in the modern business landscape.
5. Lean Staffing Plan
A Lean Staffing Plan represents a minimalist approach to workforce planning, focusing on achieving maximum efficiency and productivity with the smallest possible team. This strategy prioritizes resource optimization by emphasizing cross-training, automation, and strategic outsourcing to meet operational goals while minimizing overhead. It's a powerful model for organizations seeking to streamline operations and enhance profitability. This approach deserves its place in the list of staffing plan examples because it offers a viable alternative to traditional staffing models, particularly for resource-constrained organizations.
This method operates on the principle of maximizing the output of each employee. Instead of hiring specialists for every single function, a lean staffing plan encourages the development of multi-skilled employees capable of handling various roles. This cross-training not only reduces the need for a large workforce but also fosters a more versatile and adaptable team. Automation plays a crucial role, streamlining repetitive tasks and freeing up employees to focus on higher-value activities. Non-core functions are often strategically outsourced to specialized providers, further reducing internal headcount and allowing the core team to concentrate on the organization's primary mission. This all contributes to a flatter organizational structure with minimal hierarchy, accelerating decision-making and promoting a more agile response to market changes.
Several real-world examples showcase the successful implementation of lean staffing plans. Small manufacturing companies, particularly those employing lean production principles inspired by the Toyota Production System, often operate with lean teams where individuals are trained to work across different stages of the production process. Bootstrapped startups, inherently resource-constrained, are prime examples of how lean staffing, combined with principles from the Lean Startup methodology by Eric Ries, can drive early growth. They often rely heavily on cross-functional team members and strategic outsourcing to maximize limited resources. Professional services firms, particularly smaller consultancies, often utilize cross-trained consultants who can handle diverse client projects, and local restaurants frequently employ multi-skilled staff who can transition between kitchen duties and customer service as needed.
For businesses considering a lean staffing model, several actionable tips can contribute to successful implementation:
- Invest heavily in employee training and development: Cross-training requires a commitment to upskilling employees and providing them with the knowledge and tools necessary to succeed in multiple roles.
- Implement robust knowledge documentation systems: Centralized documentation ensures that critical information is readily accessible to all team members, regardless of their primary function.
- Create clear prioritization frameworks for tasks: With a smaller team, it's crucial to establish clear priorities and ensure that everyone understands the relative importance of different tasks. This helps prevent bottlenecks and ensures that critical activities receive adequate attention.
- Build strong relationships with outsourcing partners: Strategic outsourcing relies on reliable and competent external partners. Building strong relationships with these partners is essential for smooth operations and successful project delivery.
- Monitor employee workload and stress levels closely: While a lean team can be highly efficient, it’s important to be mindful of the potential for burnout. Regularly monitoring workload and stress levels can help identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
The benefits of a Lean Staffing Plan are numerous. Lower labor costs and reduced overhead expenses translate to higher profit margins. Increased employee versatility often leads to higher engagement as individuals are challenged to develop new skills and take on greater responsibility. The flatter organizational structure facilitates faster decision-making, and the reduced overhead contributes to greater agility and responsiveness to market changes.
However, a lean approach also presents potential drawbacks. The increased responsibilities placed on employees can lead to burnout if not carefully managed. Limited redundancy poses a risk if key employees leave, potentially disrupting operations. Service quality may suffer during peak periods due to limited staff availability. Finally, while cross-training enhances versatility, it can also lead to reduced specialization and expertise depth in specific areas, and the organization may be vulnerable to unexpected workload increases.
When is a lean staffing plan the right choice? This approach is particularly well-suited for small and medium businesses, startups and entrepreneurs, creative freelancers, marketing agencies, and local community organizations. Organizations experiencing rapid growth or operating in volatile markets can benefit from the agility and responsiveness of a lean team. It is also an attractive option for organizations seeking to minimize overhead and maximize profitability.
Learn more about Lean Staffing Plan
By carefully considering the pros and cons and implementing the tips outlined above, organizations can leverage the power of a lean staffing plan to achieve their operational goals while maintaining a streamlined and efficient workforce. This efficient approach, focused on maximizing resources and minimizing waste, offers a compelling staffing solution for organizations of all sizes, particularly those in dynamic and competitive environments.
6. Skills-Based Staffing Plan
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, traditional, role-based staffing plans often fall short. Enter the Skills-Based Staffing Plan, a dynamic approach that prioritizes specific competencies and abilities over rigid job titles. This model offers a strategic advantage for organizations seeking agility and adaptability in their workforce, making it a crucial staffing plan example for modern businesses. Instead of focusing on pre-defined roles, a skills-based approach emphasizes assembling teams with complementary skill sets, ready to tackle evolving project needs and market demands. This method allows businesses to respond quickly to new opportunities and challenges, making it particularly relevant for startups, small to medium businesses, and even larger organizations navigating digital transformation.
This methodology works by first identifying the core skills required for organizational success, both present and future. A comprehensive skills inventory of the current workforce is created, mapping existing competencies and highlighting potential gaps. Job descriptions are then rewritten with a focus on required skills rather than traditional duties. This shift facilitates internal mobility, as employees can move between projects and roles based on their skill set, rather than being confined by a specific job title. Continuous learning and development programs become central to this model, ensuring employees are constantly upskilling and expanding their competencies to meet evolving business needs.
Several organizations have demonstrated the successful implementation of skills-based staffing. IBM’s transition to skills-based hiring for cloud and AI roles exemplifies this shift, allowing them to quickly adapt to the growing demand for these specialized skills. Similarly, Accenture's focus on digital skills for consulting projects ensures their workforce remains at the cutting edge of technological advancements. The prevalence of agile development teams within tech companies is another example of skills-based staffing in action, where cross-functional teams are assembled based on the specific skills needed for each project. Even healthcare organizations are adopting this approach, cross-training nurses for multiple specialties to address fluctuating patient needs and optimize staffing resources. These examples underscore the versatility and effectiveness of skills-based staffing across diverse industries.
Implementing a Skills-Based Staffing Plan requires a strategic approach. Here are some actionable tips:
- Develop comprehensive skills assessment frameworks: Utilize a combination of methods, including self-assessments, peer reviews, and practical tests, to accurately gauge employee competencies.
- Create clear learning and development pathways: Offer tailored training programs and mentorship opportunities to help employees acquire new skills and progress along defined career paths.
- Implement skills-based performance management systems: Evaluate employees based on their demonstrated skills and contributions, rather than just fulfilling traditional job duties.
- Foster a culture of continuous learning: Encourage employees to actively pursue skill development through online courses, workshops, and internal knowledge sharing initiatives.
- Use technology platforms to track and match skills: Leverage HR technology platforms like Workday and SAP SuccessFactors to manage skills inventories, identify skill gaps, and facilitate internal mobility based on skill requirements.
Learn more about Skills-Based Staffing Plan
The advantages of a Skills-Based Staffing Plan are numerous. It enhances organizational adaptability and flexibility, allowing businesses to quickly respond to market changes and emerging opportunities. It improves employee engagement by offering clear pathways for skill development and career progression. This model also leads to better talent utilization across different projects, maximizing the return on investment in human capital. Furthermore, it reduces dependency on external hiring for new needs, saving time and recruitment costs. Finally, it strengthens succession planning by identifying and developing internal talent with high-potential skills.
However, this approach also presents some challenges. Implementing and maintaining complex skill assessment and tracking systems can be resource-intensive. There might be potential resistance to change from traditional departments accustomed to role-based structures. A higher investment in training and development programs is also necessary to support continuous learning. Standardizing compensation across varying skill levels can be complex, requiring careful consideration of pay equity and market benchmarks. Finally, if not properly managed, there's a risk of skill gaps emerging if employee development doesn't keep pace with evolving business needs.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of a Skills-Based Staffing Plan often outweigh the drawbacks, particularly for organizations operating in dynamic and competitive environments. By prioritizing skills and fostering a culture of continuous learning, businesses can build a future-ready workforce equipped to thrive in the face of change and drive sustained growth. This approach deserves a prominent place in any discussion about staffing plan examples due to its focus on adaptability, talent optimization, and long-term organizational success. This approach is particularly beneficial to startups, small and medium businesses, creative freelancers, marketing agencies, and local community organizations as it allows for flexible team structures and efficient resource allocation.
7. Succession Planning Staffing Model
A robust staffing plan is crucial for any organization, regardless of size. Among the various staffing plan examples, the Succession Planning Staffing Model stands out for its long-term strategic approach to workforce management. This model focuses on cultivating internal talent to fill critical roles within the organization, ensuring continuity and minimizing disruption. It’s an essential component of strategic workforce planning, moving beyond simply filling open positions to proactively preparing for future leadership and specialized skill needs. This approach is particularly relevant for organizations aiming for sustainable growth and stability.
The Succession Planning Staffing Model works by identifying key roles within the organization and then systematically developing internal candidates to assume those positions when they become vacant. This involves a multi-faceted approach that includes talent assessments, targeted development programs, and mentorship initiatives. It’s a continuous process that requires ongoing evaluation and adjustment to ensure the organization has a pool of qualified individuals ready to step up when needed. This model offers a powerful way to build a strong leadership pipeline and ensure the organization has the right people in the right roles at the right time, ultimately contributing to its long-term success. This deserves a place on this list because it offers a proactive, rather than reactive, approach to staffing, benefiting organizations by reducing recruitment costs, improving employee engagement, and maintaining institutional knowledge.
One of the core features of a successful Succession Planning Staffing Model is the thorough identification of critical roles and key positions. This involves analyzing the organization's structure, strategic goals, and potential future needs. Once these roles are identified, the model emphasizes robust talent assessment and potential evaluation processes to identify individuals with the aptitude and potential to fill these positions. These processes may include performance reviews, skill assessments, psychometric tests, and 360-degree feedback. The identified high-potential employees then undergo structured leadership development programs tailored to equip them with the necessary skills and experience. These programs can include formal training, on-the-job learning, job rotations, and participation in special projects. Knowledge transfer and mentoring systems are also crucial components, ensuring that institutional knowledge and best practices are passed on to the next generation of leaders. Finally, clear career pathing and internal promotion priorities are established, providing employees with a clear understanding of growth opportunities and motivating them to invest in their development within the organization.
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented succession planning. General Electric’s leadership development program under Jack Welch is a classic example, establishing a rigorous system for identifying and developing future leaders. Procter & Gamble’s strong promote-from-within culture demonstrates another successful application, prioritizing internal talent and fostering a sense of loyalty and career progression within the company. Similarly, Johnson & Johnson’s leadership pipeline programs are well-regarded for their structured approach to developing future leaders at all levels of the organization. Even government agencies often employ structured advancement paths, ensuring continuity and expertise within their ranks. These examples showcase how effective succession planning can strengthen an organization and contribute to its long-term success.
Implementing a Succession Planning Staffing Model requires a thoughtful and structured approach. First, identify critical roles and create detailed succession maps, outlining potential successors for each position. Then, implement regular talent review and assessment processes to evaluate employee potential and identify development needs. Create individual development plans for high-potential employees, outlining specific learning objectives and activities. Establish mentoring and coaching programs to provide guidance and support. Finally, remember to balance internal development with strategic external hiring to ensure a healthy influx of new ideas and perspectives.
While this model offers numerous advantages, such as ensuring organizational continuity and stability, improving employee retention and engagement, and reducing external hiring costs and risks, there are potential drawbacks to consider. It may limit the influx of external talent and fresh perspectives. It also requires a significant investment in development programs and carries the risk of internal politics and favoritism influencing selection processes. There's also the potential for skills gaps if internal candidates aren't fully prepared when a critical role becomes vacant. Finally, developing internal talent for leadership roles requires time, meaning there may be long development timelines for critical positions.
Learn more about Succession Planning Staffing Model
This model is particularly beneficial for small and medium businesses, startups, entrepreneurs, creative freelancers, marketing agencies, and local community organizations looking for long-term stability and seeking to cultivate leadership from within. By investing in their existing talent, these organizations can build a stronger future and ensure continued success. While implementing a succession planning strategy requires dedicated effort, the long-term benefits of organizational continuity, improved employee engagement, and a strong leadership pipeline make it a worthwhile investment for organizations of all sizes. By focusing on growing talent internally, you not only reduce costs associated with external recruitment but also foster a culture of development and opportunity within your team, leading to increased loyalty and a more resilient organization overall. This method provides a framework for "staffing plan examples" that emphasizes long-term growth and stability.
7 Staffing Plan Models Compared
| Staffing Plan | ⭐ Expected Outcomes / Results 📊 | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | ⚡ Resource Requirements | 💡 Key Advantages / Tips | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Project-Based Staffing Plan | ⭐⭐⭐ Cost-effective for short-term, specialized projects | 🔄 Medium – onboarding contractors, knowledge transfer | Moderate – mix of full-time and temporary staff | 💡 Clear role descriptions, plan knowledge transfer | Short-term projects, specialized expertise needs |
| Seasonal Staffing Plan | ⭐⭐⭐ Optimized for fluctuating demand, cost-efficient | 🔄 Medium – cyclical recruitment and training | High – repeated seasonal hiring/training | 💡 Early recruitment, streamlined training, incentivize returns | Retail, hospitality, agriculture during peak seasons |
| Growth-Phase Staffing Plan | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Scalable growth, maintains culture and capacity | 🔄 High – phased hiring tied to milestones | High – upfront recruitment and infrastructure investment | 💡 Tie hiring to revenue, strong employer branding | Rapidly expanding companies, startups after funding |
| Remote-First Staffing Plan | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Access to global talent, reduced overhead | 🔄 Medium – technology and remote process setup | Moderate – investment in digital tools and training | 💡 Robust communication, virtual onboarding, clear expectations | Companies embracing distributed workforces post-COVID |
| Lean Staffing Plan | ⭐⭐⭐ Efficient, low-cost, agile | 🔄 Medium – cross-training, process automation | Low to moderate – focus on multi-skilled staff | 💡 Invest in training, outsource non-core functions | Small businesses, startups, firms optimizing costs |
| Skills-Based Staffing Plan | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Highly adaptable, promotes continuous learning | 🔄 High – skills inventory, tracking, mobility systems | High – training, sophisticated HR systems | 💡 Develop skill frameworks, foster learning culture | Organizations requiring flexibility and talent development |
| Succession Planning Staffing Model | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Ensures leadership continuity, reduces turnover | 🔄 High – long-term development and mentoring | High – leadership programs and assessments | 💡 Map critical roles, create development plans | Large corporations focusing on leadership pipeline |
Finding the Right Fit for Your Creative Team
From project-based needs to long-term growth strategies, this article has explored various staffing plan examples, including project-based, seasonal, growth-phase, remote-first, lean, skills-based, and succession planning models. Understanding these different approaches is key to building a thriving and productive creative team. The most important takeaway is that there's no one-size-fits-all solution. The best staffing plan aligns with your specific goals, resources, and the nature of your work. Mastering these concepts allows you to optimize your workforce, ensuring you have the right talent at the right time, maximizing efficiency and minimizing unnecessary overhead. Managing employee leave is a crucial part of any successful staffing plan. For further insights into minimizing disruptions due to absences, explore these helpful resources on absence management strategies from LeaveWizard. Effective staffing ultimately empowers your team to reach its full creative potential and deliver exceptional results.
A well-structured staffing plan not only streamlines your workflow but also contributes to a positive and supportive work environment. By proactively anticipating your staffing needs and implementing the appropriate strategies, you can create a team that’s well-equipped to handle any challenge. Ready to build your dream creative team? Creativize connects you with top-tier creative talent, helping you find the perfect individuals to bring your staffing plan to life. Explore Creativize today and unlock the power of a perfectly staffed creative team.

