Building Your Dream Team: Why a Staffing Plan Matters
A solid staffing plan is crucial for success, ensuring you have the right people at the right time. This listicle provides six staffing plan examples to help you build your own. Learn how to create effective strategies for various situations, from healthcare facilities to startups. Discover key features, advantages, and disadvantages of each staffing plan example, along with practical tips for optimizing your team, whether you're a small business, a creative freelancer, or a large organization.
1. Healthcare Facility Staffing Plan
A healthcare facility staffing plan is a comprehensive strategy designed to ensure adequate and appropriate staffing levels within hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings. It’s a crucial element for delivering high-quality patient care while adhering to legal requirements and budgetary constraints. This type of staffing plan example differs significantly from other industries due to the 24/7 operational needs, specialized skill sets required, and stringent regulations governing patient safety and care quality. This approach hinges on accurately forecasting patient demand, understanding required skill sets, and implementing robust scheduling mechanisms. It accounts for various medical specialties, shift rotations, and legal compliance concerning patient-to-staff ratios. A well-executed staffing plan not only improves patient outcomes but also minimizes staff burnout and optimizes resource allocation.
Features of a Healthcare Facility Staffing Plan:
- Shift rotation scheduling with built-in redundancy: This ensures continuous coverage, accounting for breaks, sick leaves, and unexpected absences. Float pools and on-call staff are integral components of this redundancy.
- Skill-based role allocation: Matching staff expertise with specific patient needs is paramount. This involves assigning nurses, physicians, and other medical professionals to roles that align with their qualifications and certifications.
- Contingency planning for patient surges: Healthcare facilities must be prepared for unexpected increases in patient volume, such as during flu seasons or public health emergencies. Contingency plans outline procedures for quickly mobilizing additional staff and resources.
- Compliance tracking for healthcare regulations: Adhering to regulations like mandated patient-to-staff ratios is crucial. The staffing plan should incorporate mechanisms to monitor and document compliance.
- Seasonal adjustment mechanisms: Flu seasons and other periods of high demand necessitate adjustments to the staffing plan. These adjustments might involve increasing staff levels, extending shifts, or implementing specialized care units.
Pros:
- Ensures proper patient care coverage 24/7.
- Maintains compliance with healthcare regulations.
- Addresses specialized skill requirements of different medical departments.
- Incorporates float pools for staffing flexibility.
Cons:
- Complex to implement due to the demanding 24/7 operational requirements.
- High costs associated with employing specialized medical professionals.
- Requires frequent updates to reflect changing healthcare regulations and best practices.
- Can be challenging to balance optimal staffing levels with budget constraints.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Renowned institutions like the Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, and Kaiser Permanente provide compelling staffing plan examples. Mayo Clinic integrates physicians, nurses, and support staff across departments, fostering collaboration and efficient resource utilization. Cleveland Clinic prioritizes a patient-centered staffing model, ensuring that staffing decisions revolve around patient needs and preferences. Kaiser Permanente's integrated care team approach emphasizes interdisciplinary collaboration to deliver comprehensive care.
Tips for Creating an Effective Staffing Plan:
- Build staffing plans around peak patient care hours to ensure adequate coverage during the busiest times.
- Incorporate cross-training programs to enhance staff flexibility and enable them to fill multiple roles if needed.
- Plan for at least 15-20% more staff than the minimum requirements to account for vacations, sick leave, and other planned or unplanned absences.
- Review staffing efficacy quarterly against patient outcomes, staff satisfaction, and budgetary performance. This regular evaluation allows for adjustments and improvements.
Why This Approach Deserves Its Place in the List:
Healthcare facility staffing is a complex undertaking with unique challenges. Its inclusion in this list of staffing plan examples highlights the specific needs and considerations of this critical sector. This specialized approach is essential for ensuring high-quality patient care, maintaining regulatory compliance, and optimizing resource allocation within the healthcare environment.
Organizations like the American Nurses Association, The Joint Commission, and the Institute for Healthcare Improvement have popularized best practices and guidelines for healthcare staffing, further emphasizing the importance of this specialized approach. Learn more about Healthcare Facility Staffing Plan This link, while not directly about healthcare staffing, can offer insights into creative team management principles that can be adapted to healthcare settings.
2. Agile Software Development Team Staffing Plan
An Agile Software Development Team Staffing Plan is a dynamic approach designed to optimize the efficiency and adaptability of software development teams. Unlike traditional staffing models, which often rely on rigid roles and hierarchical structures, Agile staffing prioritizes cross-functional teams, iterative development, and flexible resource allocation. This method allows teams to quickly respond to changing project requirements, embrace continuous delivery, and foster a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement. It's a key element of a successful staffing plan example, particularly for businesses embracing modern software development practices.

This staffing plan centers around building cross-functional teams comprised of developers, QA specialists, and product owners. Instead of assigning individuals to specific tasks, resources are allocated in sprints, allowing for adjustments based on project progress and evolving priorities. T-shaped skills profiling is often used to identify team members with specialized expertise in one area (the vertical bar of the "T") and a broader understanding of other related disciplines (the horizontal bar). This encourages collaboration and reduces dependencies between specialized teams. Furthermore, Agile teams often include embedded technical specialists like DevOps engineers and UX designers, bringing critical skills directly into the core team.
This approach offers several advantages. It promotes flexibility and adaptability, enabling teams to quickly respond to changing market demands and customer feedback. This facilitates continuous delivery and iteration, allowing for faster release cycles and improved product quality. Agile staffing also encourages skill development across multiple areas, creating more versatile and valuable team members. However, it's not without its challenges. Forecasting long-term staffing needs can be difficult, and potential skill gaps may emerge during transition periods. It can also require hiring more experienced (and often more expensive) generalist developers. Performance evaluation also becomes more complex, requiring metrics that reflect the collaborative and iterative nature of Agile development.
Successful examples of Agile staffing include Spotify's squad-based model, Google's product-focused team structure, and Atlassian's balanced team approach incorporating developers, designers, and product managers. These companies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Agile staffing in delivering high-quality software products in fast-paced environments. Learn more about Agile Software Development Team Staffing Plan to gain a deeper understanding.
For those considering implementing an Agile staffing plan, here are some actionable tips: aim for 5-9 members per team for optimal communication, include at least one senior developer per team for mentorship, allocate around 20% of team time for addressing technical debt and skill development, and define explicit roles while also encouraging skill overlap. Finally, a crucial aspect is to plan staffing around product features rather than technical specialties. This product-centric approach ensures the team remains focused on delivering value to the customer.
This method is particularly well-suited for startups, small to medium businesses, and creative agencies that need to remain agile and responsive in dynamic market conditions. It empowers teams to embrace change, deliver value quickly, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. By understanding the features, benefits, and potential challenges, organizations can effectively implement an Agile staffing plan and reap the rewards of a more flexible and productive development process. This is why the Agile Software Development Team Staffing Plan deserves its place on this list of staffing plan examples.
3. Retail Seasonal Staffing Plan
A Retail Seasonal Staffing Plan is a specialized staffing plan example designed to handle the ebb and flow of personnel needs in retail businesses throughout the year. It focuses on optimizing staffing levels during peak seasons like holidays, special sales events, and predictable increases in customer traffic. This approach acknowledges that staffing needs aren't static and provides a framework for scaling up or down efficiently. This involves strategically hiring temporary staff to augment the core team during high-demand periods and reducing reliance on temporary staff during slower periods. By accurately forecasting staffing needs and implementing flexible hiring strategies, businesses can align their workforce with revenue opportunities while controlling labor costs.

This type of staffing plan deserves a place on this list because it provides a practical solution for a common business challenge: balancing customer service demands with efficient resource allocation. It’s especially relevant for retail businesses, which often experience dramatic fluctuations in customer traffic throughout the year. The key features of a successful retail seasonal staffing plan include tiered staffing levels (core, flex, seasonal positions), data-driven forecasting based on historical sales patterns, cross-training programs for staff flexibility, a blended full-time/part-time employee mix, and staggered hiring timelines for peak seasons.
Examples of Successful Implementation: Major retailers like Target, Amazon, and Macy's have effectively implemented seasonal staffing strategies. Target, for example, adds over 100,000 seasonal workers for the holiday rush. Amazon’s flex workforce model allows them to scale their logistics operations rapidly during Prime Day and other peak periods. Macy's utilizes a blend of virtual and in-store seasonal positions to meet the demands of online and brick-and-mortar shoppers.
Pros:
- Aligns staffing costs directly with revenue opportunities.
- Provides flexibility to meet changing customer demand.
- Creates clear career paths from seasonal to permanent roles.
- Leverages historical data for accurate forecasting.
Cons:
- Higher training and onboarding costs due to temporary staff turnover.
- Potential inconsistency in customer service quality.
- Challenging to maintain company culture with a large influx of temporary staff.
- Complex scheduling requirements.
Actionable Tips for Implementing a Retail Seasonal Staffing Plan:
- Begin seasonal hiring at least 60 days before anticipated peak periods.
- Create an accelerated training program specifically designed for seasonal staff.
- Implement a "return seasonal employee" program with incentives to encourage experienced seasonal workers to return the following year.
- Use split shifts during extended holiday hours to maximize coverage.
- Develop a core competency matrix to identify cross-training opportunities and enhance staff flexibility.
When and Why to Use This Approach: This staffing plan example is ideal for businesses experiencing predictable seasonal or cyclical fluctuations in demand. Retailers, hospitality businesses, and e-commerce companies can all benefit from this model. It's particularly relevant when businesses need to scale rapidly to meet increased customer demand without incurring excessive permanent staffing costs. Learn more about Retail Seasonal Staffing Plan and adapt this plan to your specific needs. The principles outlined can be adjusted to suit businesses of all sizes, from small boutiques to large retail chains.
4. Project-Based Consulting Staffing Plan
A Project-Based Consulting Staffing Plan is a dynamic approach to resource allocation, specifically designed for professional services and consulting firms. It prioritizes matching the right skills to client projects while balancing billable hours, maintaining a pool of available consultants (bench strength), and meeting utilization targets. This staffing plan example works by first identifying upcoming projects and their respective phases. Then, based on the project requirements, consultants with the necessary expertise are assigned to each phase, considering factors like expertise level (partner, manager, associate), availability, and professional development opportunities. This method allows firms to optimize their resources and deliver high-quality services to clients.
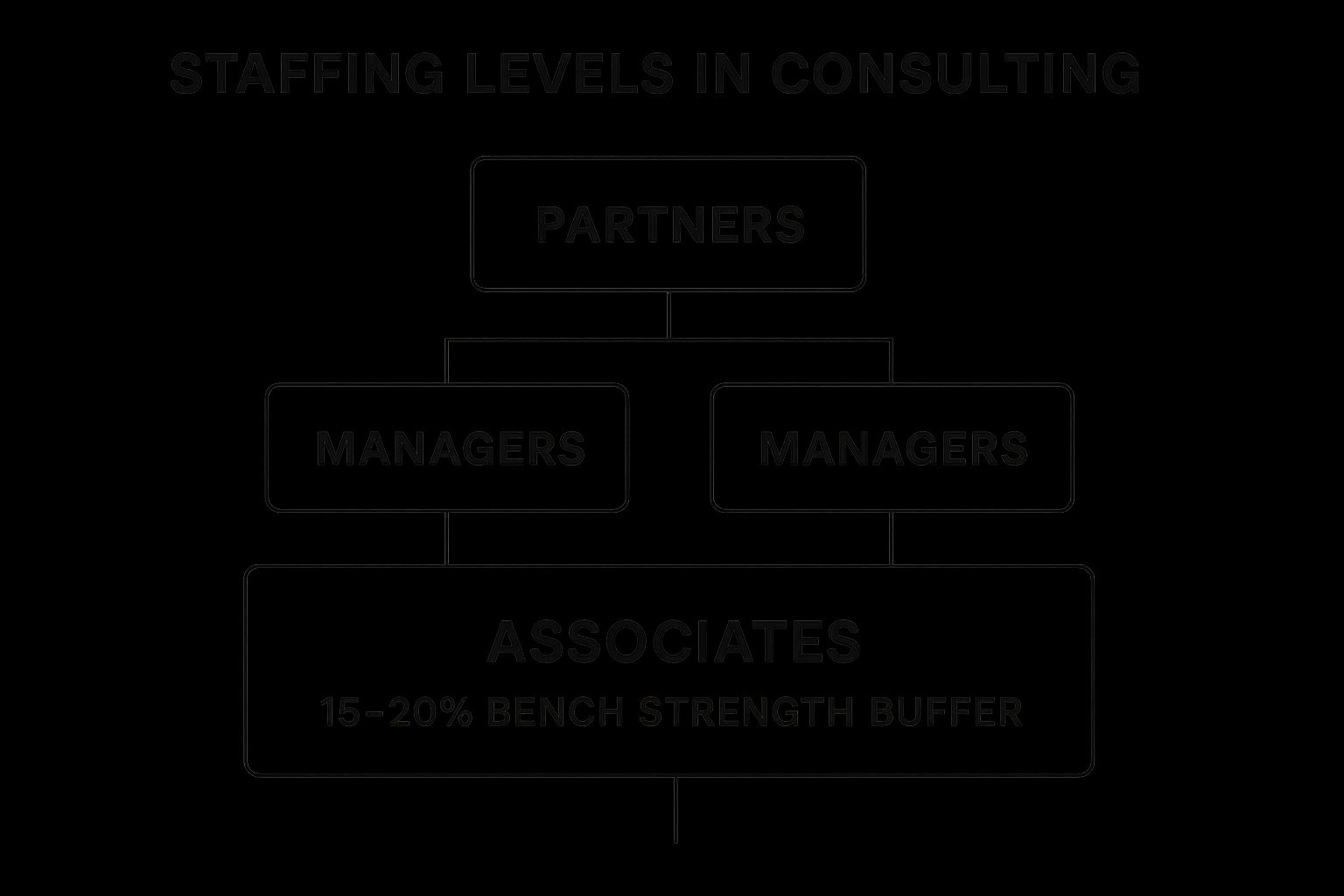
The infographic visualizes the hierarchical structure of a typical project-based consulting team. At the top are the Partners, responsible for overall client relationships and project oversight. Below them are the Managers, leading project execution and managing teams of Associates. Finally, the Associates form the base of the pyramid, performing the core project tasks. This hierarchical structure ensures clear lines of responsibility and facilitates efficient project delivery. The infographic clearly highlights the importance of balancing the distribution of roles across different expertise levels to maintain an efficient and cost-effective staffing structure.
This model offers several benefits: maximizing billable hours and revenue generation, aligning specific expertise with client needs, enabling professional development through project variety, and providing clear visibility into resource availability. Features such as skills-based resource mapping, utilization rate tracking, and phase-based staffing with ramp-up and ramp-down periods make this a robust staffing plan example. Companies like McKinsey & Company, Deloitte, and Accenture have successfully implemented similar models, showcasing their effectiveness in a real-world setting. For instance, McKinsey's clear expertise levels and Deloitte's matrix approach demonstrate how this model can be tailored to different organizational structures.
However, this approach isn't without its drawbacks. Potential resource conflicts between projects, the risk of consultant burnout from back-to-back assignments, the challenge of maintaining bench expertise without billable work, and susceptibility to staffing gaps due to project delays or cancellations are all potential downsides. Learn more about Project-Based Consulting Staffing Plan to understand how to mitigate these challenges, especially related to project scope creep and its impact on staffing.
This staffing plan example is particularly suitable for consulting firms, marketing agencies, and even startups and entrepreneurs working on multiple, time-bound projects. It provides a structured way to manage talent, optimize resources, and ensure project success. For smaller teams, adapting this model can improve efficiency and profitability.
To implement a Project-Based Consulting Staffing Plan effectively, consider these tips:
- Maintain a 15-20% bench strength: This buffer allows you to respond to unexpected project needs or staff absences.
- Implement a skills database: Quickly identify consultants with the required expertise for new projects.
- Create staffing pairs: Partner senior and junior consultants for knowledge transfer and mentorship.
- Develop rolling forecasts: Create 3-month staffing forecasts updated weekly to anticipate resource needs.
- Consider splitting consultants: Maximize utilization by assigning consultants to multiple projects, but be mindful of potential burnout.
This Project-Based Consulting Staffing Plan example deserves its place in this list due to its comprehensive approach to resource management. It offers a scalable solution for organizations of all sizes looking to optimize their staffing strategies and maximize the value of their human capital. By focusing on matching skills to projects, tracking utilization, and maintaining a healthy bench, this method provides a robust framework for successful project delivery and business growth. This is particularly relevant for the target audience of small and medium businesses, startups, freelancers, and agencies who often grapple with fluctuating project demands and limited resources. Using this model can provide them with a more strategic and adaptable approach to staffing.
5. Startup Growth Stage Staffing Plan
A Startup Growth Stage Staffing Plan is a dynamic and adaptable staffing plan example crucial for high-growth startups transitioning from their initial stages to more mature operations. Unlike traditional staffing plans that often assume a stable environment, this model acknowledges the volatile nature of startups and prioritizes both immediate needs and long-term organizational development. It's a crucial element for any startup aiming for rapid, yet sustainable, expansion. This approach recognizes that a startup's team needs evolve rapidly and requires a more fluid and responsive strategy.
This method works by tying hiring decisions directly to tangible business milestones, such as funding rounds achieved or specific revenue targets met. This ensures that growth in team size is aligned with the company's actual progress and helps conserve precious cash runway. The plan also emphasizes mapping out core functions versus those that can be outsourced, allowing the startup to remain lean and focus its internal resources on mission-critical activities. Learn more about Startup Growth Stage Staffing Plan
A key feature of this staffing plan example is its emphasis on transitioning from generalist roles, common in the early stages, to more specialized roles as the company matures. This provides clear growth paths for early employees and allows the startup to build deeper expertise in specific areas. It also incorporates the use of dual-purpose roles during early scaling, where individuals may wear multiple hats, maximizing efficiency with a smaller team. Embracing flexible work arrangements (remote, contract, full-time) is another important aspect, providing the agility needed to adapt to rapidly changing circumstances.
Examples of successful implementation:
- Airbnb: Airbnb’s journey from 3 founders to over 6,000 employees showcases the effectiveness of a flexible staffing plan. Their early reliance on contract workers and a gradual build-out of specialized teams allowed them to scale rapidly while adapting to market demands.
- Stripe: Stripe's methodical department building approach, prioritizing essential functions and scaling teams strategically as they hit specific growth milestones, is another excellent example of a successful growth stage staffing plan.
- Slack: Slack's evolution from a startup to an enterprise organization demonstrates how a flexible staffing plan can support significant growth and transformation.
Pros:
- Conserves cash runway by aligning hiring with business milestones.
- Maintains organizational agility during rapid growth.
- Allows for pivoting as the business model evolves.
- Creates clear growth paths for early employees.
Cons:
- Risk of skill gaps during critical growth periods.
- Potential for organizational confusion during transitions.
- Challenging to maintain culture while scaling quickly.
- May require frequent reorganizations.
Actionable Tips:
- Hire for cultural fit early, specialized skills later.
- Use contractors for specialized functions until full-time roles are justified.
- Create 30-60-90 day hiring roadmaps aligned with business milestones.
- Implement 'fractional' executive roles before committing to a full C-suite.
- Prioritize revenue-generating and product development roles first.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
This type of staffing plan is ideal for startups experiencing rapid growth or anticipating significant scaling in the near future. It's particularly relevant after securing seed funding or experiencing a surge in market demand. This approach provides a structured framework for managing talent acquisition during periods of rapid change, ensuring the company has the right people in the right roles at the right time. This methodical approach, popularized by resources like Y Combinator’s startup scaling guidance, Andreessen Horowitz’s talent management philosophy, and Reid Hoffman’s 'Blitzscaling' approach, helps startups navigate the complex challenges of rapid growth. This deserves a place on this list because it provides a practical and adaptable framework for managing one of the most critical aspects of startup success: building the right team at the right time.
6. Manufacturing Shift-Based Staffing Plan
A Manufacturing Shift-Based Staffing Plan is a crucial staffing plan example for businesses operating around the clock. This structured approach ensures continuous production by addressing the complexities of 24/7 operations, specialized equipment needs, stringent safety protocols, and output targets across multiple shifts. This type of staffing plan example is essential for maximizing efficiency and maintaining consistent production quality in manufacturing environments.
This method revolves around strategically allocating personnel across different shifts, typically involving 3-shift or 4-shift rotations. It intricately links staffing levels to production targets, ensuring adequate manpower for meeting output goals. A core component is the skill matrix, mapping employees' expertise to specific equipment operation, ensuring the right people are handling the right machinery. Recognizing the criticality of certain roles for safety and operational continuity, redundancy is built-in, preventing disruptions due to absences or unforeseen circumstances. Furthermore, a robust Manufacturing Shift-Based Staffing Plan integrates maintenance and quality control personnel into the shift structure, facilitating proactive equipment upkeep and real-time quality checks.
Features of a Manufacturing Shift-Based Staffing Plan:
- Multi-shift scheduling: Typically 3-shift or 4-shift rotations to ensure 24/7 coverage.
- Skill matrix mapping: Matching employee skills to specific equipment operation.
- Production target-based staffing levels: Aligning manpower with production goals.
- Safety-critical role redundancy: Ensuring backup for crucial roles to prevent disruptions.
- Maintenance and quality control integration: Incorporating these functions within the shift structure.
Pros:
- Maximizes equipment utilization and production output: Continuous operation leads to higher output.
- Creates clear shift handover protocols: Ensures seamless transitions between shifts.
- Provides comprehensive coverage for continuous operations: Meets the demands of 24/7 production.
- Establishes career progression from entry-level to specialized roles: Offers growth opportunities for employees.
Cons:
- Complex to schedule with overtime considerations: Requires careful planning and management of overtime.
- Potential for fatigue-related safety issues on night shifts: Demands attention to employee well-being and safety measures.
- Higher staffing costs due to shift differentials: Involves additional costs associated with different shift timings.
- Requires comprehensive cross-training programs: Necessitates investment in training to ensure flexibility and coverage.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Toyota Production System's team-based staffing approach: Emphasizes teamwork and flexibility within shifts.
- Tesla's manufacturing staffing model combining automation and human expertise: Integrates automation with skilled human operators.
- Procter & Gamble's high-efficiency production staffing: Focuses on streamlined staffing for optimized output.
Actionable Tips for Implementing a Manufacturing Shift-Based Staffing Plan:
- Implement at least a 10% buffer staffing for each shift: Accounts for unforeseen absences and fluctuations in demand.
- Create 'cellular' team structures around production lines: Fosters ownership and accountability.
- Develop clear career ladders from general labor to specialized positions: Motivates employees and facilitates skill development.
- Rotate shift supervisors to maintain consistent standards: Ensures uniform application of procedures and practices across all shifts.
- Cross-train at least 25% of staff on critical equipment operations: Provides flexibility and backup for key roles.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
This staffing plan example is ideal for manufacturing businesses operating 24/7 with complex processes, specialized equipment, and stringent safety requirements. It’s particularly relevant for industries like automotive, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and any sector demanding continuous production. The Manufacturing Shift-Based Staffing Plan helps achieve high efficiency, maintain consistent quality, and optimize resource utilization. Its structured approach provides a clear framework for managing the complexities of round-the-clock operations and ensuring that production targets are met consistently. This approach, popularized by Toyota Production System principles, Lean manufacturing methodologies, and Six Sigma frameworks, provides a robust foundation for achieving operational excellence in demanding manufacturing environments.
6-Example Staffing Plan Comparison
| Staffing Plan | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | 💡 Resource Requirements | ⭐ Expected Outcomes | 📊 Ideal Use Cases | ⚡ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Facility Staffing Plan | High due to 24/7 coverage and regulations | High costs, specialized medical staff | Ensures patient care and regulatory compliance | Hospitals, clinics with continuous care needs | Covers specialized skills; regulatory aligned |
| Agile Software Development Team | Moderate; requires iterative setup | Skilled cross-functional generalists | Flexible, adaptive delivery of software | Agile software development teams | Promotes adaptability; continuous delivery |
| Retail Seasonal Staffing Plan | Moderate; fluctuating seasonal demands | Mix of full-time, part-time, temporary | Aligns staffing with sales cycles | Retail businesses with variable peak seasons | Cost-effective scaling; flexible staffing |
| Project-Based Consulting Staffing | High; complex resource and skills mapping | Varied expertise levels, requires bench | Maximizes billable utilization and expertise | Consulting and professional services firms | Expertise alignment; maximizes revenue |
| Startup Growth Stage Staffing Plan | Moderate; evolves with milestones | Mix of generalists, contractors | Supports rapid scaling and agility | High-growth startups transitioning phases | Aligns hiring with milestones; conservative cash use |
| Manufacturing Shift-Based Staffing | High due to multi-shift and safety needs | Skilled operators, cross-trained staff | Maximizes production output and safety | 24/7 manufacturing plants with continuous production | Continuous coverage; enhances equipment utilization |
Power Up Your Workforce: Final Thoughts on Staffing
From healthcare facilities to agile software teams, and from retail stores to startups, a well-defined staffing plan is crucial for success. This article provided diverse staffing plan examples, including approaches for seasonal retail, project-based consulting, manufacturing, and high-growth startups. These examples offer valuable insights into matching talent with demand, optimizing schedules, and managing resources effectively. The key takeaway is that a strong staffing strategy—whether it's for a small business or a large corporation—needs to be adaptable, data-driven, and aligned with your overall business objectives.
Mastering these staffing principles isn't just about filling roles; it's about building a thriving and productive work environment. While a staffing plan focuses on the immediate needs of your workforce, consider the long-term career development of your employees. Investing in your team's growth can boost morale and retention. You can learn more about developing a detailed career plan from Academia do Universitario. By strategically allocating resources and nurturing talent, you'll empower your team to reach its full potential and drive significant results. Remember, your people are your greatest asset; invest in them wisely.
Ready to build your dream team and optimize your staffing strategy? Creativize provides a platform to connect with top creative professionals, allowing you to find the perfect talent to fill your staffing plan needs and elevate your projects. Visit Creativize today and unlock the potential of your workforce.

